The objective of this project is to determine the eccentricity of the Moon's orbit by measuring its apparent radius over a complete lunar revolution (sidereal month) around Earth. Analyzing the Moon's orbital eccentricity provides insights into the dynamics of the Earth-Moon system and variations in Earth's tidal effects. Multiple images of the moon were captured every night using a smartphone mounted on a 6-inch reflective telescope during the observation period (From 15/10/2024 to 17/11/24). The best three images of the Moon of that night captured were processed to extract its apparent radius. A plot of apparent radius versus time was then fitted using both a sinusoidal model and a Keplerian orbital model to calculate the eccentricity and other relevant parameters. While the experimentally derived eccentricity values from both fits exceeded the known literature value, the Keplerian model was observed to yield a more accurate estimate.
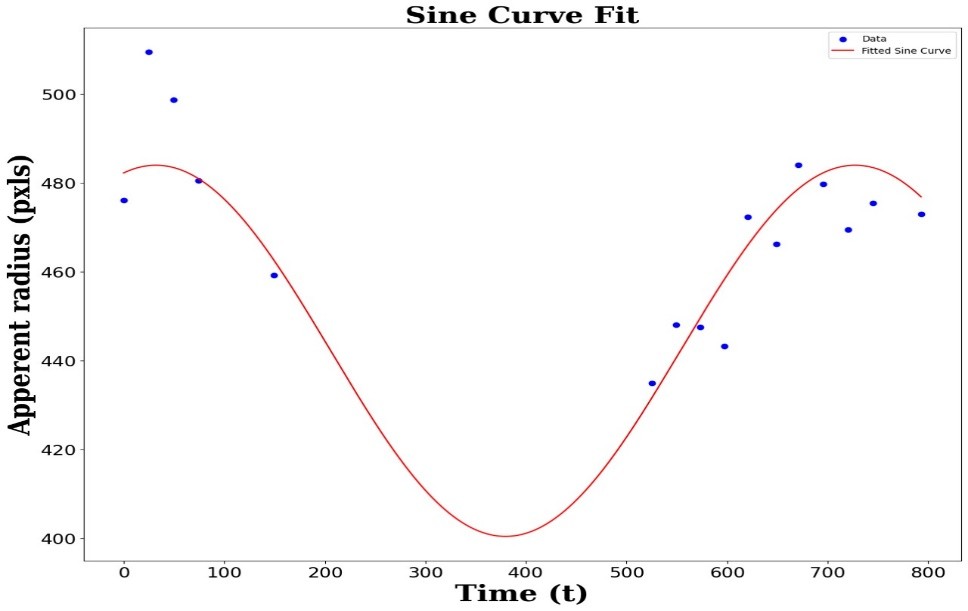
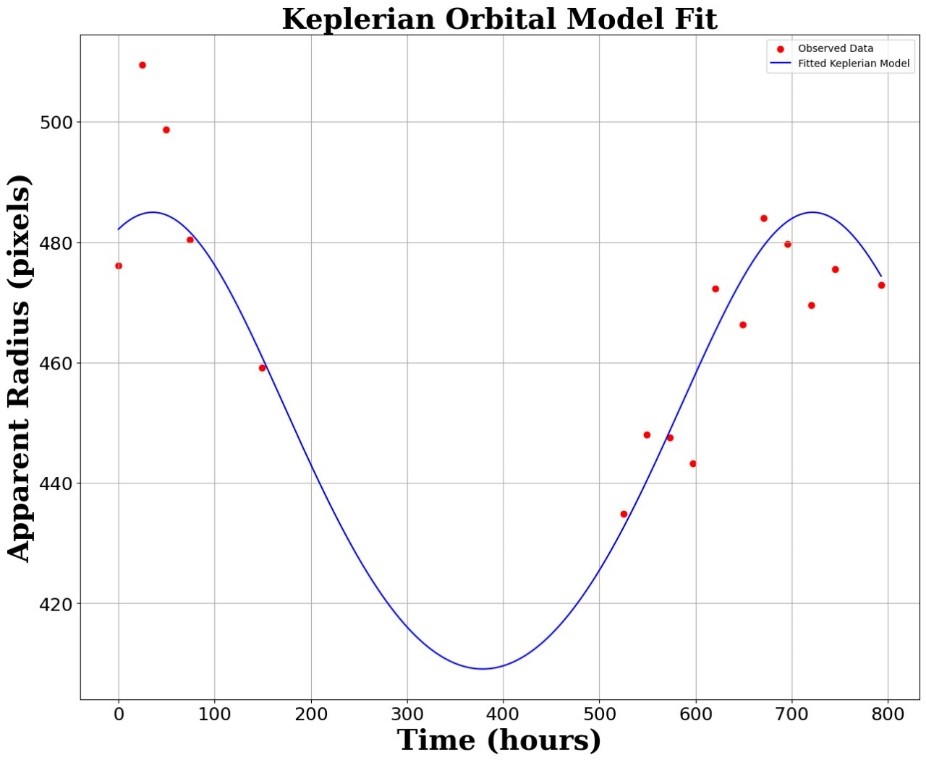
• From a general calculation using formula without any Fitting, eccentricity is 0.079. • After Sinusoidal fitting as shown in Fig. 6, eccentricity is 0.094±0.040. • After Keplerian fitting as shown in Fig.7, eccentricity is 0.084 ±0.016.
The final submissions including the findings and analysis are given here –